What is an air exchanger and how does it work
How air exchangers refresh your indoor environment
An air exchanger is a ventilation system designed to improve indoor air quality by continuously replacing stale air with fresh outdoor air. This process is essential in modern homes, which are often tightly sealed for energy efficiency but can trap pollutants, moisture, and odors inside. Air exchangers use a combination of fans and ducts to move air in and out, helping to balance humidity and reduce contaminants.
Core components and airflow process
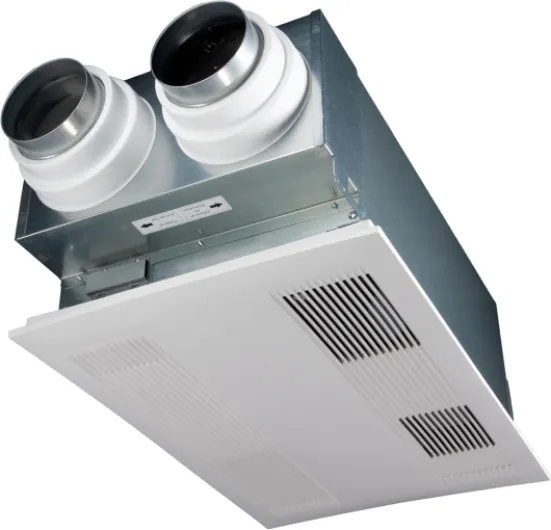
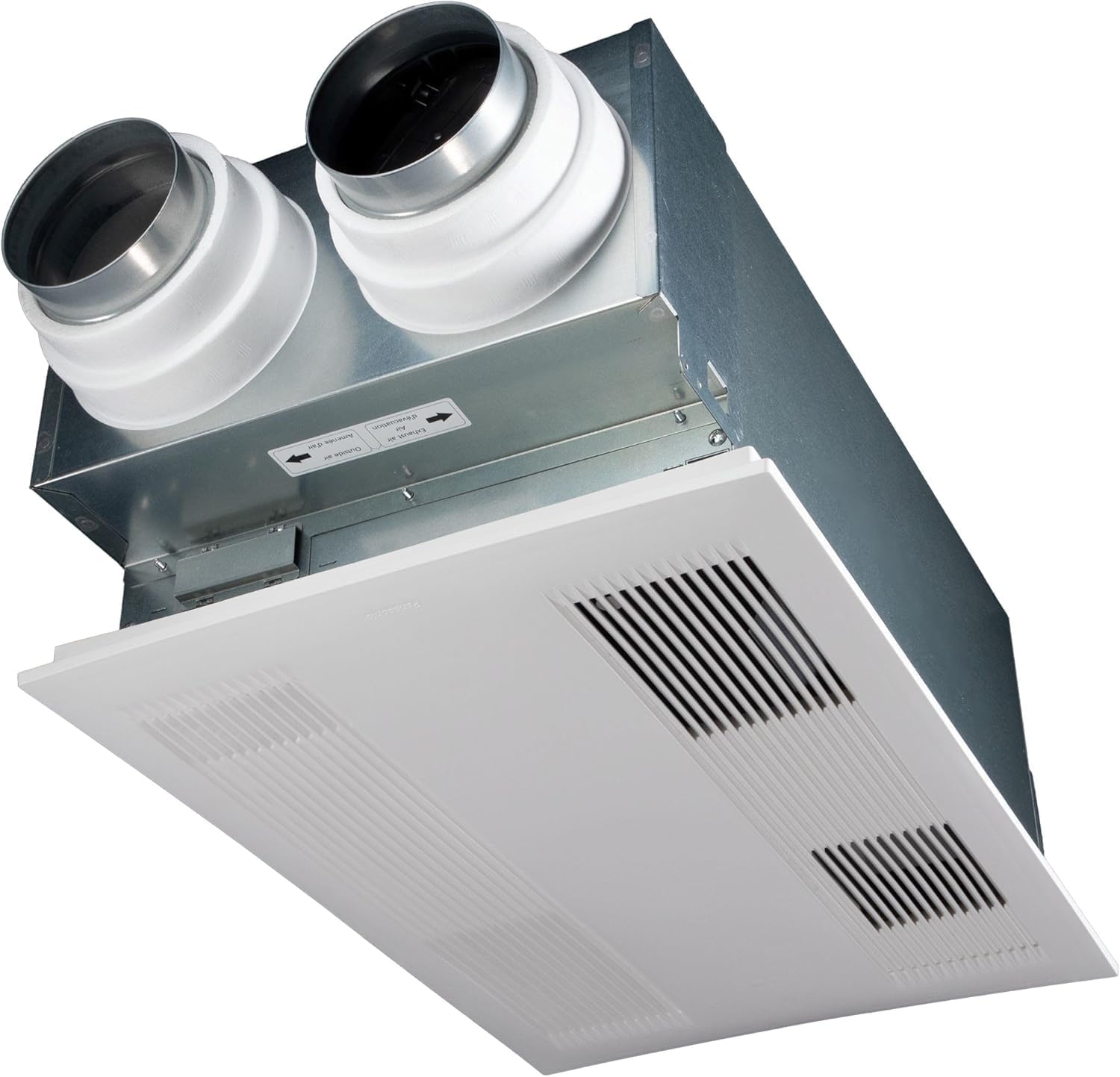
The main parts of an air exchanger include intake and exhaust vents, filters, and a heat or energy recovery core. As the system operates, it draws in fresh air from outside while expelling indoor air that may contain dust, allergens, or excess moisture. The recovery ventilator core transfers heat or energy between the outgoing and incoming air streams, which helps maintain indoor temperatures and supports energy efficiency. This means you get the benefit of improved air quality without a big impact on your heating or cooling bills.
Types of air exchangers and their functions
- Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRV): These exchangers transfer heat from outgoing stale air to incoming fresh air, making them suitable for colder climates where retaining heat is important.
- Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERV): In addition to heat, ERVs also transfer some moisture, helping to balance humidity levels. This makes them ideal for regions with varying climate conditions.
Both types are designed to work with your existing HVAC system, supporting overall ventilation and air quality throughout your home. Some products are available as standalone units, while others integrate directly with heating and cooling systems.
Why ventilation matters for health and comfort
Without proper ventilation, indoor air can become polluted with dust, pet dander, volatile organic compounds, and even mold spores. Over time, this can affect respiratory health and comfort. Air exchangers play a key role in reducing these risks by ensuring a steady supply of fresh air and managing moisture levels, which helps prevent mold growth and structural damage.
If you're interested in how air purifiers compare to air exchangers for tackling specific issues like mold, you can find more details in this guide on air purifiers and mold effectiveness.
Integration with home systems and product selection
When considering an air exchanger, it's important to look at factors like airflow capacity, compatibility with your HVAC system, and the specific climate in your area. Stock availability, price, and product features can vary, so comparing different products and recovery ventilators is a good idea. Proper installation and regular duct cleaning will also help maintain performance and extend the life of your exchanger.
Key benefits of installing an air exchanger at home
Improving Indoor Air Quality and Comfort
Installing an air exchanger can make a noticeable difference in your home's air quality and comfort. These systems work by bringing in fresh outdoor air while removing stale indoor air, which helps reduce the buildup of contaminants like dust, allergens, and moisture. This process is especially important in modern, energy-efficient homes where airtight construction can trap pollutants inside. By maintaining a steady airflow, air exchangers support a healthier indoor environment and help control humidity levels, reducing the risk of mold growth and musty odors.
Energy Efficiency and Climate Control
Air exchangers, particularly energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators, are designed to minimize energy loss during the ventilation process. These systems transfer heat or energy between incoming and outgoing air streams, which helps maintain indoor temperatures and reduces the load on your heating and cooling systems. This means you can enjoy fresh air without sacrificing energy efficiency or comfort, even during extreme weather. Over time, this can lead to savings on your energy bills and a more sustainable home.
Supporting Your HVAC System
Integrating an air exchanger with your existing HVAC system can improve overall performance. By balancing airflow and reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants, air exchangers help your heating and cooling equipment operate more efficiently. This can extend the lifespan of your HVAC products and reduce the need for frequent duct cleaning. Additionally, maintaining proper ventilation supports consistent indoor temperatures and better moisture control, which is essential for both comfort and the longevity of your home’s structure.
Health and Well-being Benefits
- Reduces exposure to airborne contaminants and allergens
- Controls indoor moisture, lowering the risk of mold and mildew
- Supports better sleep and overall well-being by providing a constant supply of fresh air
- Helps manage odors from cooking, pets, and household products
Optimizing Air Exchange for Your Space
Choosing the right air exchanger and ensuring proper installation are key to maximizing these benefits. Factors such as the size of your space, local climate, and the specific needs of your household will influence the best system for you. For more guidance on optimizing air exchange rates and improving indoor air quality, you can refer to this resource on how to use an air changes per hour calculator.
Comparing air exchangers and air purifiers
How Air Exchangers and Air Purifiers Address Indoor Air Quality
When considering ways to improve indoor air quality, both air exchangers and air purifiers are popular options. However, they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways within a home or building’s ventilation system.- Air exchangers (including energy recovery ventilators, or ERVs) work by bringing in fresh outdoor air and removing stale indoor air. This process helps control moisture, odors, and pollutants, while also maintaining balanced airflow and energy efficiency. Air exchangers are often integrated into the HVAC system, supporting heating and cooling by recovering heat or energy from outgoing air.
- Air purifiers focus on filtering and cleaning the air already inside your space. They use filters (such as HEPA or activated carbon) to capture dust, allergens, and other airborne particles, but do not exchange air with the outdoors or manage humidity levels.
Key Differences in Performance and Application
| Feature | Air Exchanger (ERV/HRV) | Air Purifier |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Ventilation, moisture control, energy recovery | Particle and pollutant removal |
| Air Exchange | Yes (brings in outdoor air) | No (recirculates indoor air) |
| Energy Efficiency | High (recovers heat/energy) | Varies by product |
| Moisture Management | Yes (controls humidity) | No |
| Integration | Part of HVAC/ventilation system | Standalone or portable |
| Maintenance | Requires duct cleaning and filter changes | Requires filter changes |
| Price Range | Higher initial cost, long-term savings | Wide range, depending on features |
Which System Is Right for Your Needs?
Choosing between an air exchanger and an air purifier depends on your specific indoor air quality goals, climate, and existing HVAC system. If your priority is to remove airborne particles like dust, pollen, or pet dander, an air purifier may be the right product. For comprehensive ventilation, moisture control, and energy efficiency, an air exchanger or energy recovery ventilator (ERV) is often the better choice. Some homes benefit from using both systems together, especially in climates with extreme temperatures or high humidity. When comparing products, consider the size of your space, the type of contaminants you want to address, and your budget. For more details on selecting the best filtration solution for your HVAC system, check out this guide on choosing the right air filter for your AC vent.Choosing the right air exchanger for your space
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Air Exchanger
Choosing the right air exchanger for your home is a decision that impacts both your indoor air quality and your energy efficiency. The right system will help maintain a healthy balance between fresh outdoor air and the removal of stale air, while also managing moisture and heat recovery. Here are some important factors to weigh before making a purchase:
- Home Size and Airflow Needs: The capacity of an air exchanger should match the square footage and layout of your space. A system that is too small may not provide enough ventilation, while one that is too large can waste energy.
- Climate Considerations: In colder climates, a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) is often preferred to retain warmth during winter. In more humid or mixed climates, an energy recovery ventilator (ERV) can help manage both heat and moisture, improving comfort and reducing strain on your HVAC system.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for products with high energy recovery rates. Efficient exchangers can lower heating and cooling costs by transferring heat between incoming and outgoing air streams.
- Integration with Existing HVAC: Some air exchangers are designed to work seamlessly with your current heating and cooling system. Check compatibility to ensure optimal performance and easier installation.
- Noise Level: Consider the sound rating of the product, especially if it will be installed near living or sleeping areas. Quieter systems can make a big difference in comfort.
- Filtration and Air Quality: Some exchangers include built-in filters to capture dust and allergens, supporting better indoor air quality. Regular duct cleaning and filter changes are essential for ongoing performance.
- Price and Stock Availability: Compare prices and check the availability of different models. Higher-end products may offer advanced features like smart controls or improved energy recovery, but even basic models can deliver significant benefits if chosen correctly.
Types of Air Exchangers and Their Applications
| Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV) | Cold, dry climates | Transfers heat from outgoing stale air to incoming fresh air, improving heating efficiency |
| Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV) | Humid or mixed climates | Transfers both heat and moisture, balancing indoor humidity and temperature |
| Basic Ventilator | General ventilation needs | Provides fresh air exchange without heat or moisture recovery |
Matching the System to Your Needs
When evaluating different air exchangers, consider your home’s unique needs and the local climate. For example, a recovery ventilator with both heat and moisture control can be a smart investment in areas with high humidity or temperature swings. Always check product specifications and consult with an HVAC professional if you’re unsure about sizing or installation requirements. This will help you achieve the best balance of air quality, energy savings, and comfort in your living space.
Installation tips and common challenges
Getting Ready for Installation
Before installing an air exchanger, it’s important to assess your home’s current ventilation system and energy needs. Make sure you have the right size and type of exchanger for your space and climate. Check product specifications and compare energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) to match your heating and cooling requirements. Stock availability and price can vary, so research products and consult with HVAC professionals if needed.
Common Installation Steps
- Choose a location with enough space for the exchanger and easy access for maintenance.
- Ensure proper ductwork layout to connect the exchanger to both indoor and outdoor air sources.
- Seal all joints and connections to prevent air leaks and maintain energy efficiency.
- Install controls and sensors for airflow and moisture regulation, if your product supports them.
- Integrate the exchanger with your existing HVAC system for optimal air quality and comfort.
Challenges to Watch Out For
- Space limitations: Some homes have limited room for ductwork or the exchanger unit itself. Compact models or flexible ducting may help.
- Climate considerations: In cold climates, heat recovery is crucial to prevent heat loss. In humid areas, moisture control is key to avoid mold.
- Compatibility: Not all exchangers work seamlessly with every HVAC system. Double-check product compatibility before purchase.
- Noise: Some ventilation systems can be noisy. Look for products with quiet operation ratings.
- Professional installation: DIY installation can be challenging, especially for complex systems. Hiring a certified HVAC technician ensures proper setup and safety.
Tips for a Smooth Setup
- Plan for regular duct cleaning to maintain air quality and system performance.
- Keep the exchanger’s filters and components accessible for easy maintenance.
- Monitor airflow and adjust settings as needed for your indoor environment.
- Register your product for warranty and support from the manufacturer.
Maintenance and care for long-lasting performance
Routine Tasks to Keep Your Air Exchanger Running Smoothly
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure your air exchanger delivers optimal indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Over time, dust, moisture, and other particles can accumulate in the system, affecting airflow and the overall performance of your ventilation system. Here are some practical steps to keep your exchanger in top shape:
- Filter Cleaning and Replacement: Check your air exchanger’s filters every one to three months, depending on your climate and the manufacturer's recommendations. Dirty filters can reduce airflow and strain the system, impacting both air quality and energy recovery.
- Inspecting the Core: The energy recovery ventilator (ERV) or heat recovery ventilator (HRV) core should be inspected and cleaned at least once a year. This helps maintain efficient heat exchange and prevents the buildup of contaminants that can reduce energy efficiency.
- Duct Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate in the ducts, especially if your home is under renovation or if you have pets. Schedule professional duct cleaning as needed to maintain healthy indoor air and efficient airflow.
- Check for Moisture: Excess moisture in the system can lead to mold growth and poor air quality. Make sure the drainage system is clear and functioning, especially in humid climates.
- Monitor Airflow: Regularly check that fresh air is entering and stale air is being expelled. Blocked vents or reduced airflow can compromise the effectiveness of your ventilation system.
Common Issues and How to Address Them
Even with proper care, air exchangers can face challenges. Here are some typical issues and solutions:
- Unusual Noises: Rattling or buzzing sounds may indicate loose components or debris in the fan. Turn off the system and inspect for obstructions or contact a qualified HVAC technician.
- Reduced Airflow: If you notice less fresh air or increased humidity indoors, check for clogged filters or blocked vents. Replacing filters or cleaning vents often resolves the issue.
- Frost Build-Up: In colder climates, frost can form in the heat recovery core. Many modern products have defrost cycles, but if frost persists, ensure the system is set up correctly for your climate and consult your installer if needed.
- Odors: Persistent odors may signal a need for filter replacement or duct cleaning. If the smell continues, inspect the system for moisture or mold.
Maximizing Longevity and Performance
To get the most out of your air exchanger, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance and use. Schedule annual professional inspections to check the heat recovery ventilator, ERV, or other components. This not only extends the life of your product but also ensures your indoor air remains fresh and healthy, supporting your home’s heating, cooling, and ventilation needs year-round.
Staying on top of maintenance also helps you avoid unexpected repair costs and ensures your investment in air quality and energy efficiency pays off over time. For those comparing different products or considering upgrades, keeping your current system in good stock and condition can help you make informed decisions about future ventilation solutions.